Morquio Syndrome
What is Morquio Syndrome?
Morquio syndrome is a genetically transferable inherited disorder related to deficiency of essential enzymes. The two enzymes namely N-acetyl-galactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase (Morquio A) or enzyme beta-galactosidase (Morquio B) are responsible for metabolism of the substances which body cannot use. Absence of these enzymes leads to unwanted storage of lysosomes, especially glycosaminoglycans in the different tissues and produce different abnormalities.
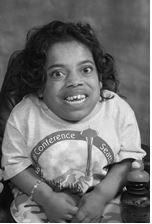
Image 1: Morquio syndrome
Alternatively, this disorder is termed as mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS IV), as glycosaminoglycans previously known as mucopolysaccharides. Depending upon the enzyme deficiency, Morquio syndrome is divided into two types:
- Type A: lack of the enzyme N-acetyl-galactosamine-6-sulfate sulfatase causing faulty degradation of of carbohydrates molecules. This includes glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulphate, which gather in different body tissues. This is more severe than Type B.
- Type B: lack of the enzyme beta-galactosidase with increase load of keratan sulfate in different body tissues causes this disorder.
Causes
Parental gene transportation leads several types of inherited disease; one of the examples is Morquio syndrome.
This genetic defect, specifically Type A Morquio syndrome is an autosomal recessive disease. For development of this disease, both the parents should have faulty genetic sequences, which will transfer to their child and causes Type A Morquio syndrome.
The deficiency of responsible enzymes is caused due to significant genetic heterogeneity with 180 mutations expressed for the GALNS gene. Abnormal mutation is also occurs in GLB1 gene.
Keratan sulphate is an example of glycosaminoglycan. Accumulation of keratan sulphate in the bones and cartilages cause major abnormalities occurs in the skeleton system.
Symptoms
All the symptoms of Morquio syndrome are almost shown within early childhood. Expected detection of abnormalities is seen after 1 year of the age of the child.
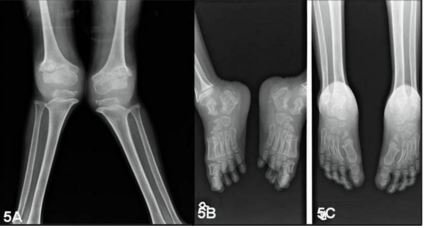
Image 2: Rediographic description of Morquio syndrome
Symptoms associated with skeleton system: The X-ray of skeleton system provides following symptoms which include:
- distinct flattening of the spine
- the arms and legs bones including humerus and femur are typically shorter and thicker than usual
- Loose-fitted joints,
- Unusual undersized neck, or
- Joint malformations like knock-knees.
- The skull size is larger in comparison with the other bodily structure.
- The association between the 1st and 2nd vertebrae present at the neck does not properly fused with each other and this deformity can be fatal.
Symptoms associated with chest:
- Increased strain which causes load on the heart and lungs.
- Respiratory collapse.
- Distortion of the chest, which include abnormal distinction of the breastbone or deformity of the lower ribs.
Symptoms associated with facial appearance:
- Size of the head is bigger than the normal
- Wide mouth
- Distinct cheekbones
- An uncommonly small nose
- Far and wide gaped and thin enamelled teeth
- Far and widely detached eyes with restrained corneal blur.
- Other included symptoms
- Slightly enlarged liver and spleen.
- Growth retardation in childhood.
- Instability in major body joints which provides unusual
- Mental development and aptitude are typically normal.
- Commonly hearing impairment develop due to high frequency sound.
Treatment
Patients having Morquio’s syndrome need customized multidisciplinary treatment management. Most symptoms are arises at the early aged, it is necessary for parents should follow all the necessary management to support their child to grow with this deformity disorder. The included treatment, management process includes:
- Genetic counselling,
- Physiotherapy,
- Supportive therapies, and
- Surgical Orthopaedic interventions
All these therapies and interventions help to improve the patient’s quality of life, duration of survival and reduce the chances of development of further extension and complications of the disease.
The specialized team of orthopaedic experts conducted the following interventions which will be beneficial for the patient’s stability:
- The surgical intervention at the first and second vertebrae provides strength and stability.
- To maintain the long bone structures of the lower extremities, including hip joint mobility, surgery (femoral osteotomy) may be beneficial for patients to help them to continue walking at the later stage of adulthood. Otherwise, they need help of wheelchairs.
- Knee replacement surgery may need to conduct at the adult age of the patient, as most of the patient suffers from arthritis and severe pain.
- Research is continuing to discover new medical therapy to treat this disease effectively. Medical researchers are getting the prospective positive approaches by replacing the enzyme and other possible treatments include gene therapy, immunosuppressive therapy, stem cell therapy, but these all need more clinical evidence.
Life Expectancy
Most of the patients have a life expectancy between 20 -30 years of age due to severe symptomatic complication arises like respiratory cessations or compression at the first two vertebrae. If the symptoms are mild then normal survival is possible.
Morquios syndrome Pictures



References
- https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001206.htm
- morquios-syndrome investigations, complications, management and prognosis at http://patient.info/doctor/morquios-syndrome
- Morquiosity.com: Morquio A Syndrome, Get The Facts at http://www.morquiosity.com/
- http://www.webmd.com/children/morquio-syndrome
- https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/morquio-syndrome/




Hey Jesse, noticed your pic here and was so interesting to read about your syndrome. I notice your wearing the Seattle conference shirt. Lol